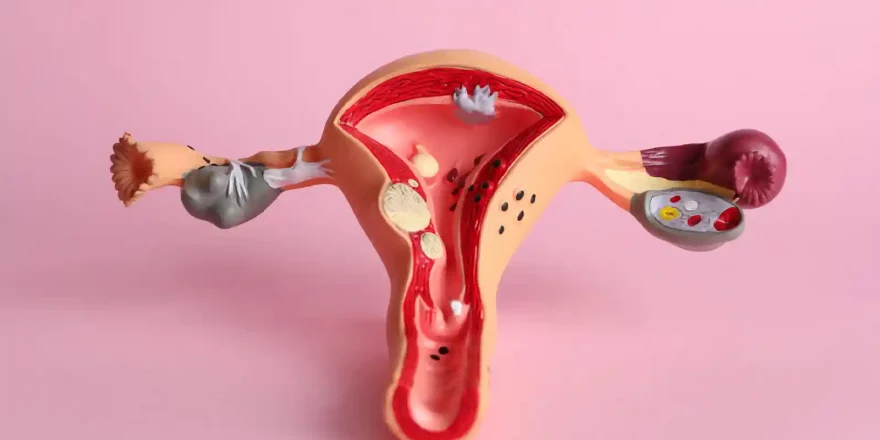
The uterus, Fallopian tubes and ovaries are the crucial organs for women’s fertility. While the ovaries release the eggs and sex hormones which control the function of the other organs, significant events happen in the uterus and Fallopian tubes. Eggs and sperm fertilise in the ends of Fallopian tubes, and embryos grow to 100 cells as th...
Eggs and Age
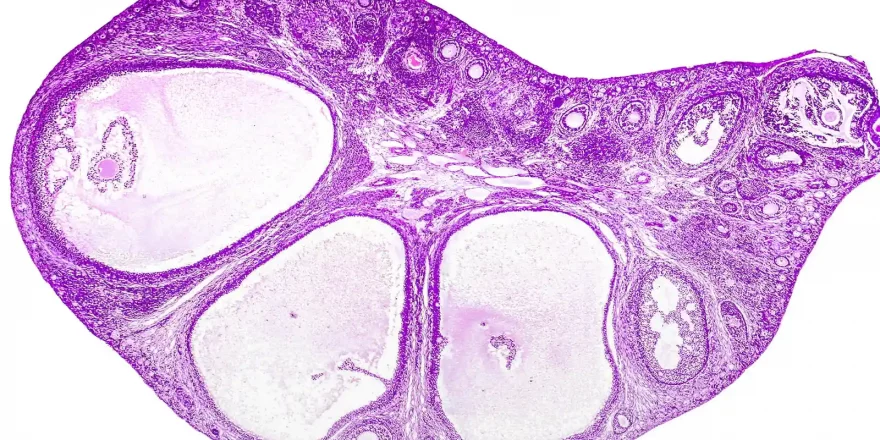
Egg numbers are a defining issue for female fertility, and most eggs in the ovaries are in an immature state as ‘primordial follicles’. All a woman’s eggs were made during her time as an embryo in the womb, and they develop more when follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) activates them. Once they’re activated, the eggs and tiny follic...
Eggs and Follicles
Eggs and follicles are core issues for a woman’s fertility, and the only time their numbers increase is during a few months when baby girls are in the womb. The eggs then remain dormant and immature in tiny ‘primordial follicles’ (which are a bit like a “flat-pack” that can safely store eggs for 50 years or more) until pubert...
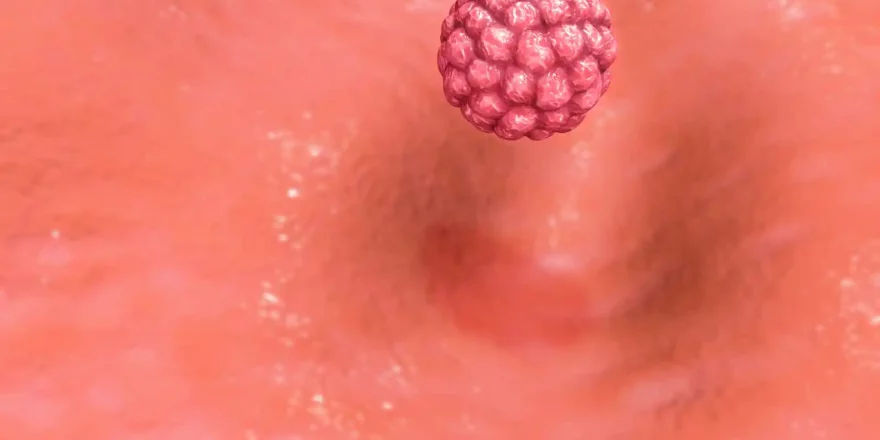
Implantation
Ovulation is the start of the process that hopefully ends in implantation, and ovulation is a dramatic event like a small volcano erupting! The “dominant follicle” that contains the egg fills rapidly with fluid, a blister forms on its surface and the egg is expelled in about 15ml of fluid. The tentacle-like ends of the Fallopian tube “sweep” ...
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
There are actually four phases in the menstrual cycle, although it’s usually divided into two phases of about 14 days each, with the period and ovulation marking the beginnings and ends of them: The “follicular phase” starts with the period and ends at ovulation The “luteal phase” begins at ovulation and ends wit...