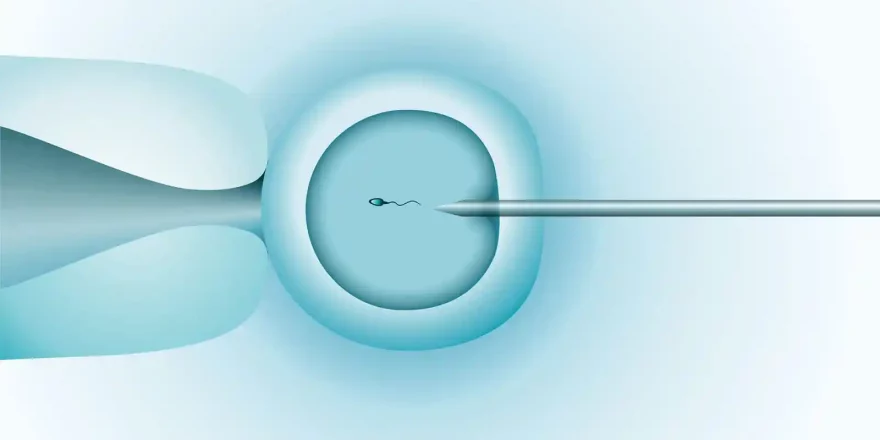
The Sperm Penetration Assay (SPA) checks to see if a man’s sperm can penetrate and fertilize eggs, and the SPA test is usually only performed when low IVF fertilization rates occur without any other explanation. For sperm to fertilize an egg, they need to physically bind with the outer layer of the egg cell (the zona pellucida) and then ...
Changing Male Fertility
Male fertility is changing, and men are becoming less fertile and the average man produces less semen and fewer sperm per ml with each passing decade. Semen samples from men born in 1925 had about 4x the number of sperm compared to samples taken in 2005. ii When the size of semen samples is compared in the last century, there’s a clear t...
Glossary
Glossary of medical terms Adhesions: internal scar tissue attachments in fibrous bands to the surfaces of organs and tissues that often result from an injury or infection. Amenorrhea: a lack of menstruation for at least three months without a pregnancy. Androgens: sex hormones such as testosterone, which are in much higher levels in men than w...
Age and Fertility
Age alters conception rates because hormone levels, sexual reserves and structures change over time. This is true for both sexes, and most women experience a gradual fall in fertility from their late teens to about 32 as egg numbers fall. This trend escalates from about 35, as egg numbers become increasingly important. i However, male fertilit...
Emotions and Fertility
Emotions directly affect fertility levels, which can be a challenge, as getting pregnant is both an emotional and a physical journey. The emotional ride varies from person to person, but after a year of trying and no conception, the emotional journey gets tougher for everyone. The word “infertility” starts to be used, and expectati...
Exercise and Fertility
Exercise directly affects health and fertility, making it a great tool to improve hormone levels, adjust weight and reduce appetite. Excess weight is the problem most people face, and increasing exercise improves the fertility of most men and women, but we’re not all the same, and this isn’t true for everyone. The morefertile® Pers...
Sperm & Organs
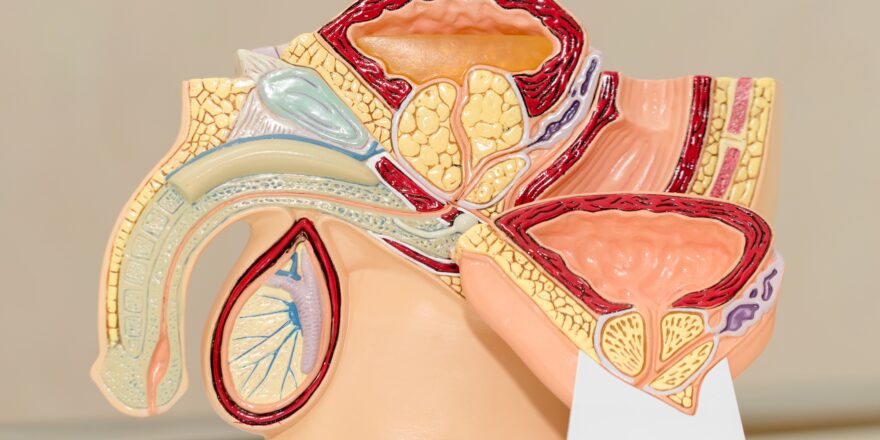
Male sexual function is much simpler than a woman’s, and it revolves around the single purpose of getting large numbers of healthy sperm to reach an egg. Most male sexual organs are outside (rather than inside) the pelvic cavity and consist of four parts: Testes (testicles) held in scrotal sacs Genital ducts Accessory glands The penis Fig 1...
The Uterus & Fallopian Tubes
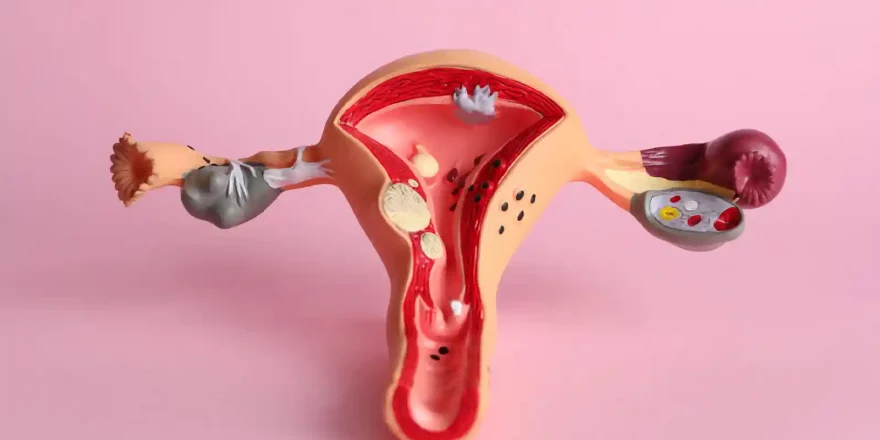
The uterus, Fallopian tubes and ovaries are the crucial organs for women’s fertility. While the ovaries release the eggs and sex hormones which control the function of the other organs, significant events happen in the uterus and Fallopian tubes. Eggs and sperm fertilise in the ends of Fallopian tubes, and embryos grow to 100 cells as th...
Eggs and Age
Egg numbers are a defining issue for female fertility, and most eggs in the ovaries are in an immature state as ‘primordial follicles’. All a woman’s eggs were made during her time as an embryo in the womb, and they develop more when follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) activates them. Once they’re activated, the eggs and tiny follic...
Implantation
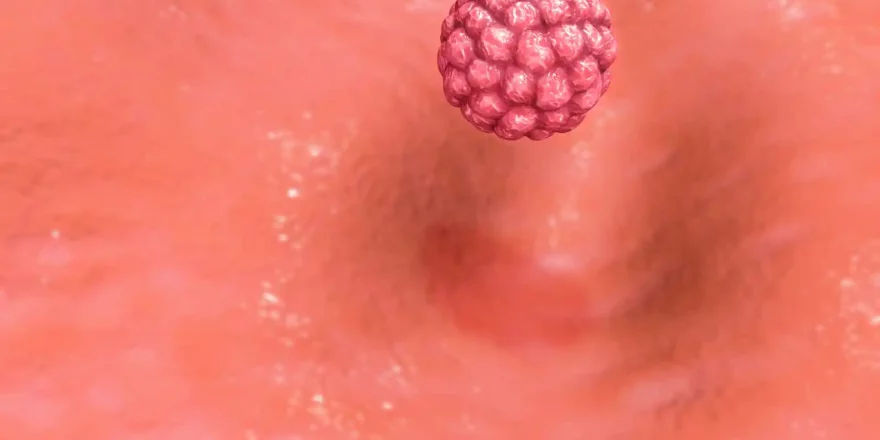
Ovulation is the start of the process that hopefully ends in implantation, and ovulation is a dramatic event like a small volcano erupting! The “dominant follicle” that contains the egg fills rapidly with fluid, a blister forms on its surface and the egg is expelled in about 15ml of fluid. The tentacle-like ends of the Fallopian tube “sweep” ...