The advice after miscarriage is usually “don’t panic”, and most miscarriages are due to one-off chromosomal abnormalities that have little bearing on future pregnancies. This is why miscarriages aren’t routinely investigated unless they are consecutive, irrespective of maternal age or fertility problems. However, an alternative approach has be...
Anovulation Treatments
Anovulation (a lack of ovulating) can be caused by a wide range of issues and is affected by lifestyle, diet, medication and exercise. It’s by far the most common condition that affects women who go to fertility clinics, and about 70% of the time, it’s PCOS, but there are five other causes of the condition. Luteinised unruptured f...
Miscarriage Causes & Treatments
The only type of miscarriage that can be treated successfully during pregnancy is a threatened miscarriage, as inevitable, missed or incomplete miscarriages can’t be saved. If a miscarriage is suspected, seek medical advice at the local “early pregnancy unit”, and the signs of threatened miscarriage are usually: Mild bleeding Cramping a...
Long & Short Protocols
The Long & Short IVF protocols are the stimulation protocols that are most commonly used, and the difference is GnRH down-regulation or not. A birth control pill (Lupron) controls the menstrual cycle and prevents ovulation in the Long Protocol, and both cycles then have stimulation from either follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or human me...
Luteal Phase Defect Treatment
Luteal phase defect treatment (LPD) is complicated because there are multiple causes of this condition, and a number of associated conditions that also reduce fertility. There’s a range of effective treatments and self-help options for many of the causes, but it’s crucial to diagnose the condition first, which is confirmed when: L...
Thyroid & Fertility
Thyroid disorders are easily overlooked, but they’re crucial fertility conditions, especially hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) which is more common than hyperthyroidism. It reduces male libido and sperm count, but has even more significant effects on female fertility and increases the chances of the following conditions: Abnormal...
IVM
In-Vitro Maturation (IVM) is a variation of conventional IVF, where the big difference is the collection and use of immature eggs. It’s a relatively new protocol (since about 2008) and clinics are still perfecting the retrieval and maturation of immature eggs and the receptivity of the womb lining for implantation. i In IVM, immature eggs are ...
IUI and Natural Cycle IVF
(ART), and IUI is usually a couple’s first line of treatment, with three to six treatment cycles being the standard before IVF is recommended. The success rates for IUI (with Clomid) and IVF are very similar; however, trying naturally is more successful than either for couples with unexplained infertility! i Intra-Uterine Insemination (...
ICSI – Female
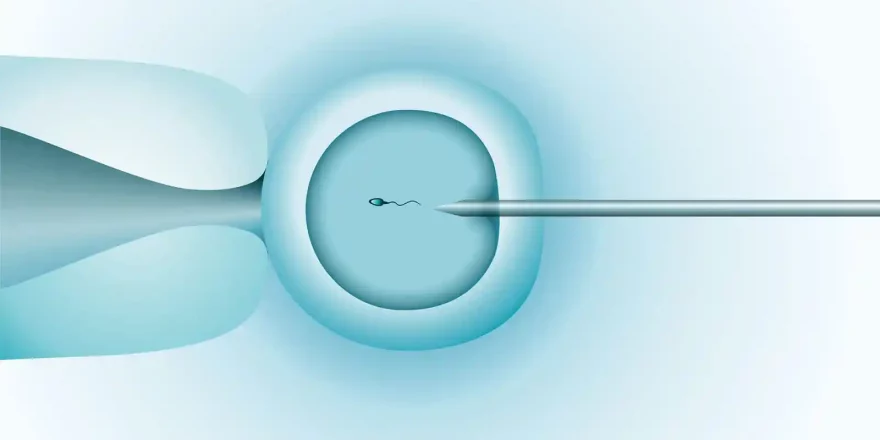
Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) has probably been the most significant development in IVF since it began in 1992. The advantage of ICSI is that as long as some sperm can be obtained (even in low numbers), a man can be a biological father. The technique has revolutionised male factor infertility and often removed the need for donor spe...
Flare Protocols
There are two Flare Protocols, and they’re usually chosen after a poor response to previous treatments or blood results show low ovarian reserve. The “Flare” or “Antagonist” protocol doesn’t suppress the pituitary gland before stimulation, and this gets a better response for women with low ovarian reserve. This pr...