Additional blood tests to rule out conditions often seen alongside PCOS and to find the cause of the condition is recommended. Blood tests are usually very accessible, and the five tests morefertile recommends are: Fasting glucose Fasting glucose (blood sugar) levels (or other tests for glucose intolerance and insulin resistance) are efficient...
Symptoms & Conditions
Polycystic ovary syndrome causes a range of symptoms because of abnormal hormone levels, including changes to menstrual cycle patterns and an increased risk of other health conditions. Hormones The crucial feature of PCOS is elevated androgens (male hormones), particularly testosterone. However, other hormones are involved in the condition, an...
Types of Polycystic Ovaries
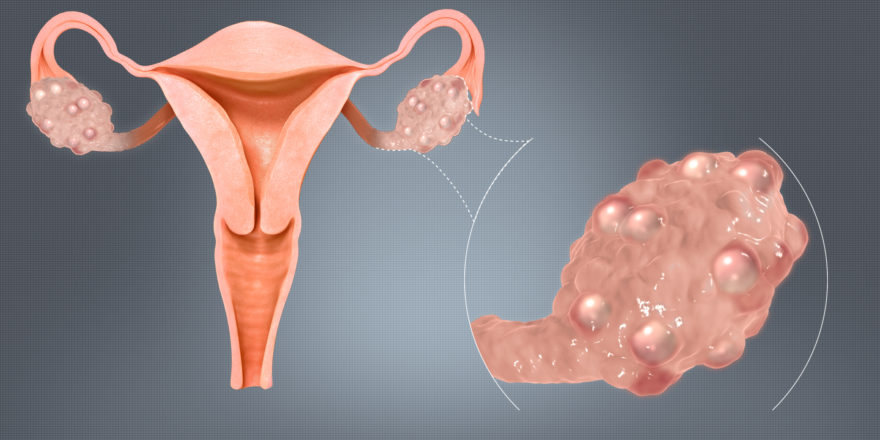
There are different types of polycystic ovaries, and which type a woman has makes a huge difference to her chances of conceiving. Millions of women have polycystic ovaries, but they don’t all have fertility issues because it can be perfectly normal for them to have many large follicles in their ovaries (the “cysts”). The problem as far as con...
Diagnosis Criteria
The diagnosis of PCOS is a problem as more than one criteria are in use, and diagnosis rates vary significantly between them. The other issue is our understanding of PCOS has also changed considerably in the last five years, plus there are significant issues using the same criteria for adults and teenagers. Most clinicians use the Rotterdam Cr...
Diagnosis of PCOS
The diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is based on the hormonal, structural and metabolic changes that drive the condition. However, there is a lot of confusion around the diagnosis, which isn’t helped by there being three internationally recognised diagnostic criteria being in use, with significantly different diagnosis rates...
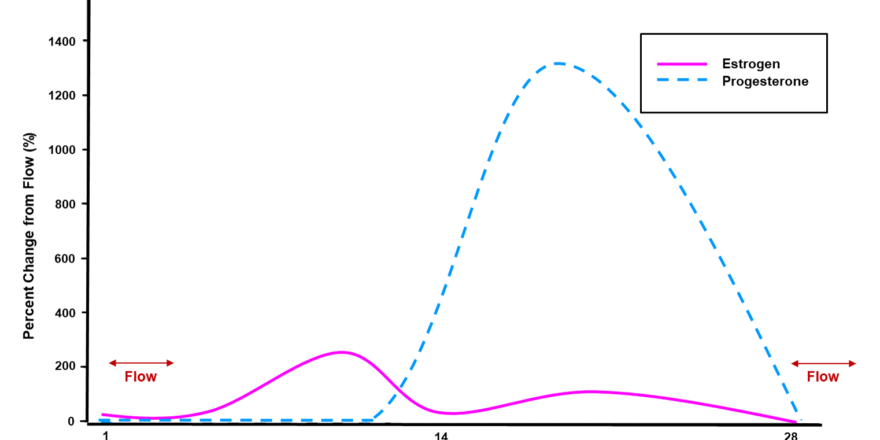
Abnormal Hormone Levels
Hormone levels are a central aspect of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and exposure to hormones as a foetus has significant consequences for the girl as an adult. Elevated androgens and Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) as a foetus alter the hormonal balance of girls after they reach puberty. However, adult hormones are heavily influenced by die...
Inflammation
Inflammation is a core part of PCOS, even though irregular ovulation, high testosterone and abnormal ovaries are the stand-out features of the condition. i For many (but not all) women the inflammation is closely linked to obesity and insulin resistance: 80% of obese PCOS women have insulin resistance 30-40% of lean PCOS women have insulin re...
Development in the Womb
A baby girl’s development in the womb significantly affects her chances of having PCOS as an adult. There are two ways a baby’s development while in the womb can later affect the baby girl as an adult. The baby’s womb environment is heavily influenced by what’s going on in the mother’s body, especially her hormone balance, and pregnant women ...
Causes of PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a complex condition that’s promoted by four significant factors: 1. Development in the womb 2. Chronic Inflammation 3. Abnormal hormone levels 4. Ethnicity and genetic predisposition Photo by Thought Catalog on Unsplash
Ethnicity & Genetics
Ethnicity and genetic predispositions to a wide range of conditions and abilities affect us all, and there are clear interactions between ethnicity and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as well as the influence of lifestyle and diet on the condition. Despite much research, no specific genes for PCOS have been found, but the daughters and sist...